Unraveling the Power of Virtualization: A Comprehensive Guide
Summary
Introduction
In the dynamic realm of technology, virtualization stands as a bedrock, reshaping our approach to computing resources. Originating in the late 1960s at IBM, virtualization has undergone a profound transformation, allowing multiple operating systems and applications to coexist on a single physical machine. This blog aims to unravel the intricacies of virtualization, catering to both beginners and seasoned engineers.
Understanding Virtualization
Virtualization, at its core, empowers a single physical machine to host multiple operating systems and their corresponding applications concurrently. This is achieved by sharing common hardware resources such as CPU, memory, and devices. The magic unfolds with the creation of virtual machines (VMs), each behaving as if it possesses exclusive access to the entire set of hardware resources. Facilitating this orchestration is the virtualization layer, often referred to as the hypervisor, which adeptly manages the allocation and sharing of resources among the various guest operating systems.
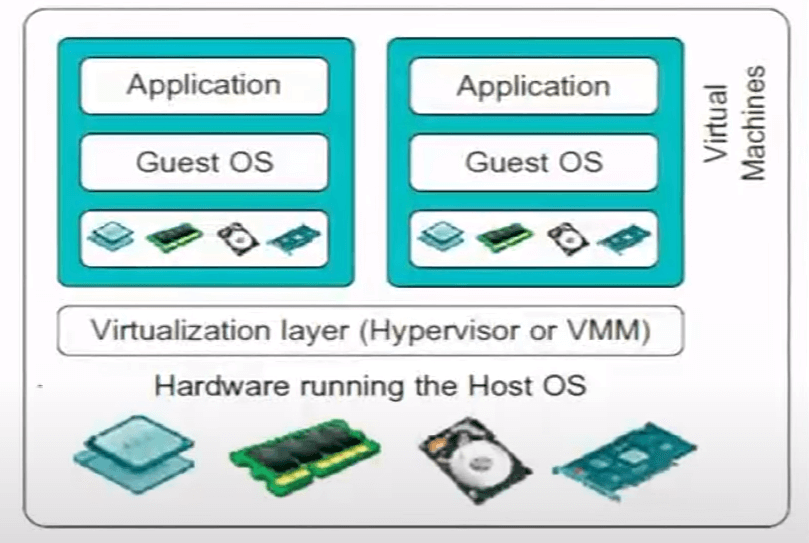
Hypervisor (Virtualization Layer)
The hypervisor, acting as a virtual machine monitor (VMM), assumes the role of an operating system responsible for overseeing multiple guest operating systems. Its primary goals include ensuring fidelity, minimizing performance impact, and maintaining complete control and safety to prevent interference among guest operating systems. This robust layer efficiently isolates each VM, providing a virtualized perspective of hardware resources.
Benefits of Virtualization
-
Consolidation: One of the paramount advantages of virtualization is consolidation. Multiple VMs seamlessly share resources on a single physical platform, leading to a reduction in hardware costs and enhanced resource manageability.
-
Migration: Virtualization facilitates the migration of VMs between physical machines. This capability amplifies availability, reliability, and performance through manageable maintenance practices.
-
Security: The encapsulation of VMs contributes to heightened security by containing malicious behavior. This ensures that security issues within one VM do not propagate to affect others.
-
Additional Benefits: Beyond the core advantages, virtualization offers benefits such as ease of debugging, support for legacy operating systems, and the effective functioning of older systems on newer hardware.
Virtualization Models
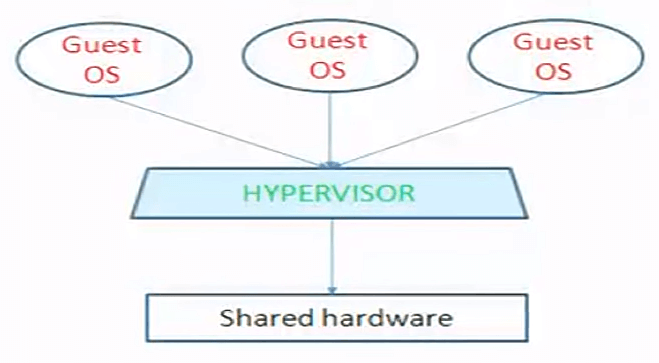
Bare-Metal Hypervisor
Sitting directly above hardware, the bare-metal hypervisor efficiently manages resources for multiple guest operating systems simultaneously. This model is renowned for its efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
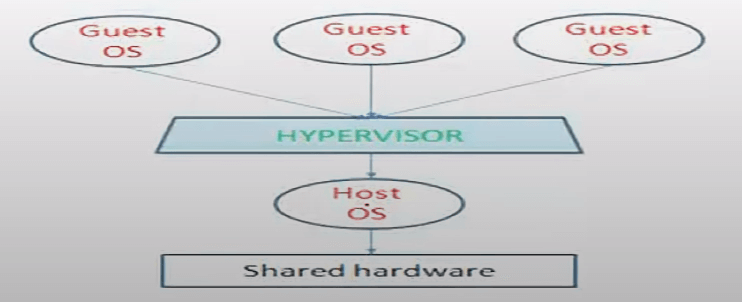
Hosted Hypervisor
In contrast, the hosted hypervisor requires the host operating system to share resources through an additional virtualization layer. This allows the simultaneous operation of multiple guest operating systems on a single machine.
Conclusion
In conclusion, virtualization emerges as a powerhouse, offering cost savings, increased efficiency, and the ability to run multiple operating systems on the same hardware through different virtualization models. As technology advances, embracing and understanding virtualization becomes not just an option but a strategic imperative for businesses and individuals alike. Whether you’re a novice exploring the landscape or an advanced engineer optimizing resource utilization, virtualization remains a key player in shaping the future of computing.
Reference: Virtualization - NPTEL