Doubly Circular Linked List | C++ Implementation
The nodes in a linked list are connected through pointers. Pointers represent the address of a location in a memory. The order in a linked list is determined by a pointer in each node. A node in a doubly circular linked list contains a data item and two node pointers, one to the previous node and one to the next node. In doubly linked list we can traverse in both direction.
Related: Doubly Linked List
Here is a meme to understand Circular Linked List.

The first node of the linked list is the head and the last node is the tail. If head is NULL then the list is empty.
In C++, a node can be defined using struct, which contain a data item and node pointers.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
struct Node
{
T data;
Node * next;
Node * prev;
Node(T value) : data(std::move(value)),
next(nullptr),
prev(nullptr)
{}
};
Node(T val): data(val), next(nullptr), prev(nullptr) {} is the constructor for the struct Node which is used to initialise data, next and prev. T means it is a generic struct and data can store values of all data types.
To declare head and tail: Node *head, *tail;
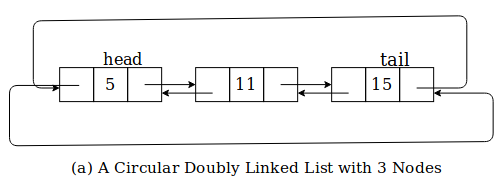
In the above fig. Node containing 5 is head and node containing 15 is tail. prev pointer in head points to the last node and next pointer in tail points to the head.
Implementation
The three basic operations supported by a linked list are searching, insertion and deletion.
Searching
In the search function a value is passed as an argument and its node is returned if found, otherwise a message says “No such element in the list” and nullptr is returned.
The function starts searching from the head to the last node and passed value is matched with every node’s data item.
Here is the code for iterative search.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
struct Node *search(T value)
{
Node *node = head;
while(node->next != head)
{
if(node->data == value)
{
return node;
}
node = node->next;
}
if(node->data == value)
{
return node;
}
std::cerr << "No such element in the list \n";
return nullptr;
}
Insertion
insert function insert a node with the value at the end of the linked list. If the linked list does not contain any node then the new node becomes head and tail otherwise new node is added after tail and its prev pointer points to tail and next pointer points to head. Then new node becomes tail.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
void insert(T value)
{
Node *node = new Node(value);
if(head == nullptr)
{
node->next = node;
node->prev = node;
head = node;
tail = node;
}
tail = head->prev;
tail->next = node;
node->prev = tail;
node->next = head;
head->prev = node;
tail = node;
}
Deletion
In deleteNode function the value is entered which is to be deleted. The function search the node containing the value using search function and then the node is deleted.
If the searched node is head then node next to head is made head and then the searched node is deleted. The node is deleted only if the value exists means if (node != nullptr).
After deletion next and prev pointer of previous and next nodes are updated.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
void deleteNode(T value)
{
Node *node = search(value);
if(node == nullptr)
{
std::cerr << "No such value in the list\n";
return;
}
else
{
Node *tmp = head;
Node *tail = head->prev;
if(tmp == node)
{
tail->next = tmp->next;
tmp->prev->next->prev = tail;
head = tail->prev;
delete tmp;
return;
}
else if(tail == node)
{
Node *curr = tail;
tmp = tail->prev;
tmp->next = curr->next;
head->prev = tmp;
tail = tmp;
delete curr;
return;
}
else
{
while(tmp->next != head)
{
if(tmp == node)
{
tmp->prev->next = tmp->next;
tmp->prev->next->prev = tmp->prev;
delete tmp;
return;
}
tmp = tmp->next;
}
}
}
}
C++ Implementation of Circular Doubly Linked List
In C++ implementation of this program we have copy constructor, move constructor, copy assignment operator, move assignment operator and destructor.
Because the presence of a user-defined destructor, copy-constructor, or copy-assignment operator prevents implicit definition of the move constructor and the move assignment operator, any class for which move semantics are desirable, has to declare all five special member functions. This is called Rule of Five.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
#include <iostream>
#include <utility>
template <typename T>
class circular_doubly_linked_list
{
struct Node
{
T data;
Node * next;
Node * prev;
Node(T value) : data(std::move(value)),
next(nullptr),
prev(nullptr)
{}
};
Node *head, *tail;
public:
circular_doubly_linked_list() : head(nullptr),
tail(nullptr)
{}
//copy constructor
circular_doubly_linked_list(const circular_doubly_linked_list &);
//copy assignment
circular_doubly_linked_list& operator=(const circular_doubly_linked_list& cdll)
{
circular_doubly_linked_list temp(cdll);
temp.swap(*this);
return *this;
}
//move constructor
circular_doubly_linked_list(circular_doubly_linked_list&&) noexcept;
//move assignment
circular_doubly_linked_list& operator=(circular_doubly_linked_list&& cdll) noexcept
{
cdll.swap(*this);
return *this;
}
~circular_doubly_linked_list();
void append_node(T);
void delete_node(T);
friend void swap(circular_doubly_linked_list& lhs, circular_doubly_linked_list& rhs)
{
std::swap(lhs.head, rhs.head);
}
template <typename U>
friend std::ostream & operator<<(std::ostream & os, const circular_doubly_linked_list<U> & cdll)
{
cdll.print_list(os);
return os;
}
private:
struct Node *search(T value)
{
Node *node = head;
while(node->next != head)
{
if(node->data == value)
{
return node;
}
node = node->next;
}
if(node->data == value)
{
return node;
}
std::cerr << "No such element in the list \n";
return nullptr;
}
void print_list(std::ostream& os = std::cout) const
{
Node *tmp = head;
while(tmp->next != head)
{
std::cout << tmp->data << ' ';
tmp = tmp->next;
}
std::cout << tmp->data << '\n';
}
};
template <typename T>
circular_doubly_linked_list<T>::circular_doubly_linked_list(const circular_doubly_linked_list & cdll)
{
if(cdll.head == nullptr)
{
head = tail = nullptr;
}
else
{
head = new Node(cdll.head->data);
Node *curr = head;
Node *tmp = head;
Node *obj_curr = cdll.head;
while(obj_curr->next != cdll.head)
{
curr->next = new Node(obj_curr->next->data);
obj_curr = obj_curr->next;
curr = curr->next;
curr->prev = tmp;
tmp = tmp->next;
}
tail = curr;
curr->next = head;
head->prev = curr;
}
}
template <typename T>
circular_doubly_linked_list<T>::circular_doubly_linked_list(circular_doubly_linked_list&& cdll) noexcept
{
head = tail = nullptr;
swap(*this, cdll);
}
template <typename T>
void circular_doubly_linked_list<T>::append_node(T value)
{
Node *node = new Node(std::move(value));
if(head == nullptr)
{
node->next = node;
node->prev = node;
head = node;
tail = node;
}
tail = head->prev;
tail->next = node;
node->prev = tail;
node->next = head;
head->prev = node;
tail = node;
}
template <typename T>
void circular_doubly_linked_list<T>::delete_node(T value)
{
Node *node = search(value);
if(node == nullptr)
{
std::cerr << "No such value in the list\n";
return;
}
else
{
Node *tmp = head;
Node *tail = head->prev;
if(tmp == node)
{
tail->next = tmp->next;
tmp->prev->next->prev = tail;
head = tail->prev;
delete tmp;
return;
}
else if(tail == node)
{
Node *curr = tail;
tmp = tail->prev;
tmp->next = curr->next;
head->prev = tmp;
tail = tmp;
delete curr;
return;
}
else
{
while(tmp->next != head)
{
if(tmp == node)
{
tmp->prev->next = tmp->next;
tmp->prev->next->prev = tmp->prev;
delete tmp;
return;
}
tmp = tmp->next;
}
}
}
}
template <typename T>
circular_doubly_linked_list<T>::~circular_doubly_linked_list()
{
if(head)
{
Node *tmp = head;
while(tmp->next != head)
{
Node *t = tmp;
tmp = tmp->next;
delete t;
}
delete tmp;
head = nullptr;
}
}
int main()
{
circular_doubly_linked_list<int> cdll1;
cdll1.append_node(3);
cdll1.append_node(4);
cdll1.append_node(5);
cdll1.append_node(6);
cdll1.append_node(7);
cdll1.append_node(8);
std::cout << cdll1;
cdll1.delete_node(6);
std::cout << cdll1;
circular_doubly_linked_list<int> cdll2(cdll1); // using copy constructor
std::cout << "Linked List 2: " << cdll2;
circular_doubly_linked_list<int> cdll3 = cdll1; //using copy assignment
std::cout << "Linked List 3: " << cdll3;
circular_doubly_linked_list<int> cdll4 = std::move(cdll2); //using move constructor
std::cout << "Linked list 4: " << cdll4;
}
View this code on Github.
Get this post in pdf - Doubly Circular Linked List
Reference:
Introduction to Algorithms
The Algorithm Design Manual
Data Structures and Algorithms Made Easy
may also like
Move all Odd numbers after Even numbers in Singly Linked List
Merge two sorted Linked List (in-place)
Split Singly Circular Linked List
Reverse the Linked List
Finding Length of Loop in Linked List
Singly Linked List